AI is transforming how we address climate change by improving energy use, tracking emissions, and protecting ecosystems. Here’s a quick overview of 9 AI tools making an impact:
- DeepMind Climate Forecasting: High-accuracy weather predictions, improving renewable energy efficiency and disaster response.
- Google Environmental Insights Explorer: Tracks city-level emissions, solar potential, and urban tree coverage to help reduce carbon footprints.
- IBM Environmental Intelligence Suite: Real-time environmental monitoring and carbon tracking for businesses.
- CarbonTracker AI: Monitors emissions in real time across industries and supply chains.
- Climate TRACE: Tracks global emissions using satellite data and AI, identifying pollution sources.
- Aurora Solar AI: Speeds up solar panel installations with precise roof modeling and energy optimization.
- WindAI for Wind Farms: Enhances turbine performance and maintenance, cutting costs and boosting output.
- Rainforest Connection AI: Detects illegal logging and tracks endangered species with acoustic monitoring.
- Wildlife Insights: Analyzes camera trap images to monitor wildlife and support conservation efforts.
These tools showcase how AI is helping reduce emissions, optimize resources, and protect ecosystems. However, balancing AI's energy consumption with its benefits is crucial as we continue to innovate.
Quick Comparison
| Tool | Key Function | Impact Area |
|---|---|---|
| DeepMind Climate Forecasting | Weather predictions | Renewable energy, disaster response |
| Google EIE | City emissions tracking | Urban planning, carbon reduction |
| IBM EIS | Environmental monitoring | Business operations, risk management |
| CarbonTracker AI | Emissions tracking | Industry, supply chains |
| Climate TRACE | Global emissions tracking | Policy-making, pollution sources |
| Aurora Solar AI | Solar panel optimization | Renewable energy |
| WindAI | Wind turbine performance | Energy production, maintenance |
| Rainforest Connection AI | Forest monitoring | Ecosystem protection |
| Wildlife Insights | Wildlife tracking | Conservation, climate research |
Let’s explore each tool in detail.
Harnessing AI To Fight Climate Change
1. DeepMind Climate Forecasting
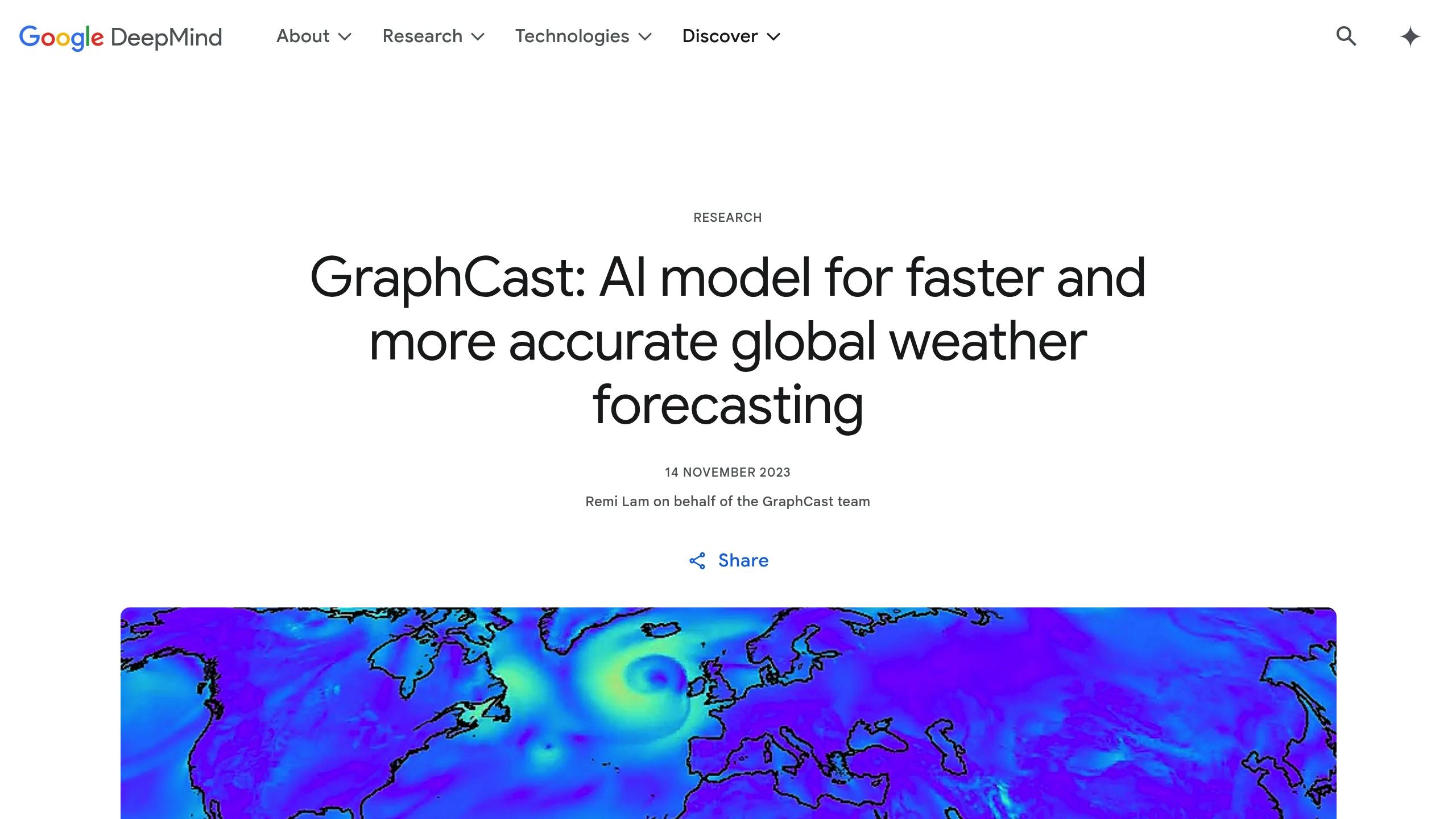
GraphCast uses graph neural networks (GNNs) to deliver detailed weather forecasts, offering high-resolution predictions (28 km x 28 km, or roughly 17.4 miles x 17.4 miles) at the equator.
This system generates 10-day forecasts in under a minute on a single Google TPU v4, making it about 1,000 times more energy-efficient than traditional high-resolution methods like HRES.
In testing, GraphCast outperformed conventional forecasting systems in over 90% of 1,380 variables, achieving 99.7% accuracy for tropospheric predictions. For instance, it accurately forecasted Hurricane Lee's landfall nine days in advance, while traditional methods confirmed it only six days prior.
"Weather forecasting is on the brink of a fundamental shift in methodology", says Sarah Dance, Professor of Data Assimilation at the University of Reading. Peter Dueben, head of Earth system modeling at ECMWF, adds, "It showed that these models are so good that we cannot avoid them anymore".
GraphCast has practical uses across key areas that directly impact climate change efforts:
| Sector | Impact on Climate Change Efforts |
|---|---|
| Renewable Energy | Improves solar and wind energy efficiency by accurately forecasting weather conditions. |
| Event Logistics | Aids in better planning and management of events with precise weather data. |
| Emergency Response | Enhances preparation for extreme weather, helping to save lives and reduce disaster impacts. |
Using data from just two points - six hours ago and the present - it predicts weather in six-hour intervals for up to 10 days. With its open-source design, GraphCast empowers researchers and forecasters worldwide. Up next, see how Google's Environmental Insights Explorer leverages AI for deeper environmental analysis.
2. Google Environmental Insights Explorer
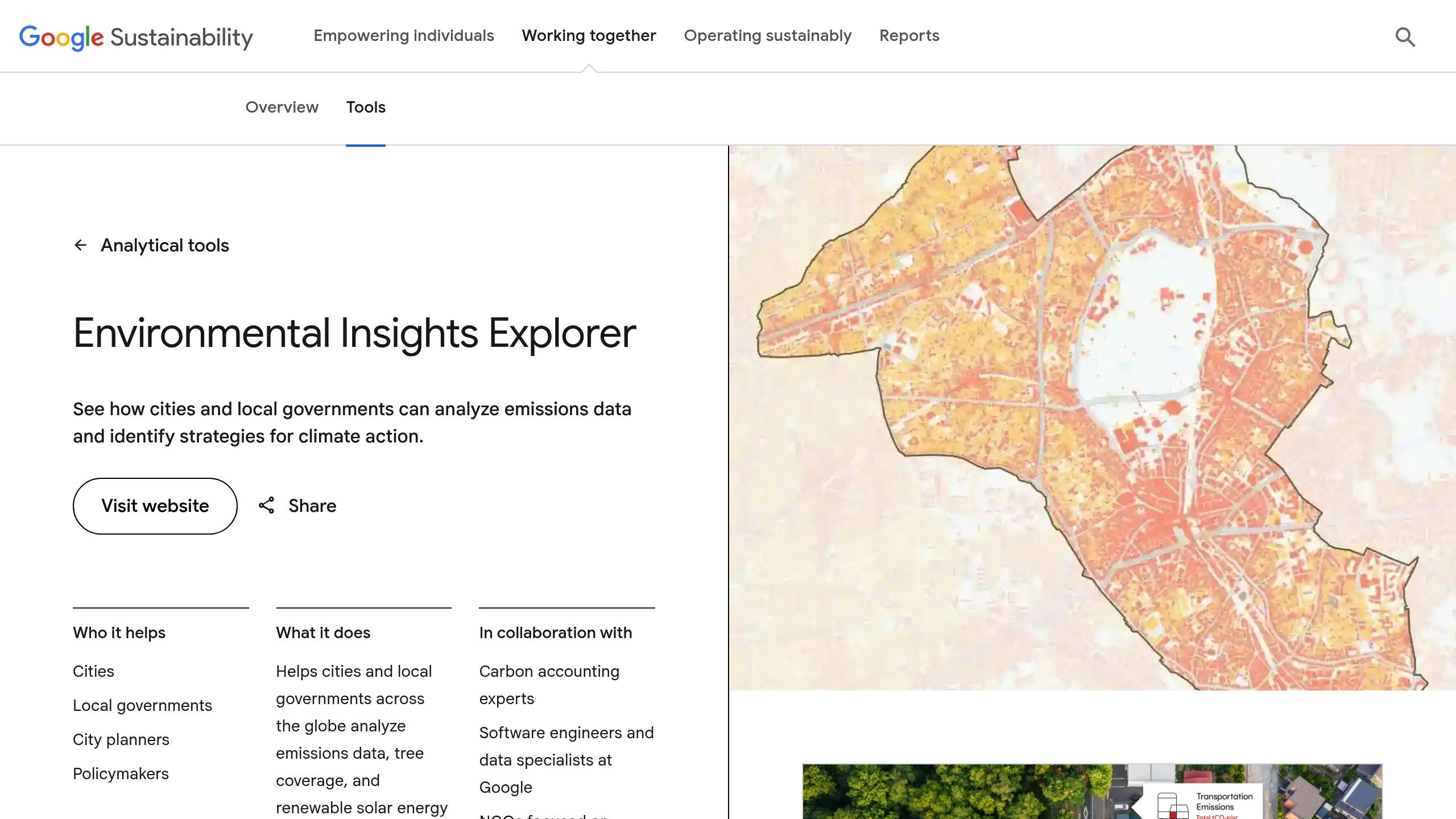
Google's Environmental Insights Explorer (EIE) combines AI and machine learning to help cities monitor and reduce carbon emissions. By integrating Google Maps data with public emissions records, the platform provides detailed insights in four areas: building emissions, transportation emissions, solar potential, and tree canopy.
EIE creates greenhouse gas (GHG) inventories using real-world activity data. It processes vast amounts of transportation and infrastructure information through advanced machine learning to deliver useful insights.
Here’s how EIE organizes city-level emissions data:
| Category | Data Provided | Impact on Climate Action |
|---|---|---|
| Building Emissions | Estimates from Google Maps data | Highlights areas for improving energy efficiency |
| Transportation | Transit patterns and emissions analysis | Supports better planning to lower transit emissions |
| Solar Potential | Rooftop solar generation capacity | Guides renewable energy adoption strategies |
| Tree Canopy | Urban forest coverage | Aids in natural carbon sequestration efforts |
Currently, fewer than 20% of the 9,000+ cities involved in the Paris Agreement have completed their GHG inventories. Traditional methods for creating these inventories can take months or even years and cost hundreds of thousands of dollars.
"This data being made available across our three cities by Google will make a substantial difference to our efforts and will help us target specific areas to achieve greater results", says Andy Street, Mayor of West Midlands.
Several cities have already shown how effective EIE can be. For example, San Jose used EIE data in its 2019 city-wide GHG inventory and plans to include it in future inventories and dashboards. Similarly, San Antonio analyzed EIE's 2020 transportation data to assess initiatives aimed at increasing bus usage.
"The most useful thing about EIE data is that it's based on real-world data and updated annually", says Yael Kisel, Climate Smart Analytics Lead at the City of San Jose.
Cities can access EIE data for free and even customize it with their own information. This makes it a versatile tool for tracking and achieving climate goals. Its AI-powered approach offers consistent baselines globally, enabling cities to create evidence-based policies and measure their progress.
In 2018, Buenos Aires used EIE to gather precise data on transportation emissions and solar energy potential. These insights helped the city design more effective emissions reduction strategies.
Next, learn how IBM's Environmental Intelligence Suite expands on AI-driven climate tools.
3. IBM Environmental Intelligence Suite
IBM's Environmental Intelligence Suite (EIS) leverages AI to provide real-time environmental monitoring and predictive analytics, helping businesses manage climate risks. In 2021 alone, the 20 largest U.S. weather events caused $145 billion in damages.
EIS combines three key components:
| Component | Function | Business Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Weather Forecasting | Hyperlocal predictions and live monitoring | Prepares businesses for extreme weather events |
| Climate Risk Analytics | Comprehensive vulnerability assessments | Highlights risks in infrastructure and supply chains |
| Carbon Tracking | Automated greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions tracking | Simplifies compliance and reporting efforts |
This platform supports industries such as utilities, manufacturing, and renewable energy. For example, utility companies use EIS to prepare for storms, improve grid reliability, and cut down on outage durations and maintenance costs.
One standout feature is the carbon performance engine, which calculates emissions across the value chain. This allows businesses to monitor emissions internally and across their supply chains, generate performance data, meet regulatory standards, and align with sustainability objectives.
"IBM Environmental Intelligence Suite provides AI-powered climate insights to help enterprises build sustainable, resilient operations. It unifies weather, climate, and geospatial data for accurate forecasting and risk assessment. Industry-specific analytics enable businesses to anticipate disruptions, streamline decision-making, and meet sustainability goals. EIS offers a centralized platform to monitor, predict, and respond to environmental impacts." - Bankai Infotech
EIS has gained traction among businesses, with 96% of executives now incorporating weather data into their operational strategies. This is critical, as the World Economic Forum's Global Risks Report 2022 highlights climate inaction as one of the gravest risks.
The platform also includes geospatial analytics, which display environmental data on interactive maps. These tools incorporate satellite imagery and sensor data for real-time monitoring. For technical teams, APIs and a Python SDK make it easy to customize the suite’s features.
With configurable alerts and an intuitive monitoring dashboard, EIS provides actionable insights and recommendations, empowering businesses to better understand and reduce their environmental footprint.
Up next, learn how CarbonTracker AI takes emissions monitoring to the next level.
4. CarbonTracker AI
CarbonTracker AI brings automated carbon emissions monitoring to the forefront, offering real-time tracking for industrial processes and supply chains.
Here’s how its three core components work:
| Component | Functionality | Business Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Production Monitoring | Tracks manufacturing emissions in real time | Pinpoints opportunities to cut emissions immediately |
| Supply Chain Analysis | Provides complete visibility of emissions across supply chains | Helps businesses choose suppliers wisely |
| Regulatory Compliance | Automates reporting and documentation | Ensures compliance with ESG regulations |
This system is designed to enhance emissions tracking and support real-time monitoring across industries.
Beyond industrial applications, CarbonTracker AI monitors hardware power usage and energy carbon intensity during deep learning tasks. It supports a variety of hardware setups, including Intel CPUs, NVIDIA GPUs, and Apple silicon. Importantly, it operates in separate threads to avoid slowing down performance.
For companies using AI and machine learning, CarbonTracker AI evaluates the environmental costs of training models. Between 2012 and 2018, the computing power needed for deep learning skyrocketed by 300,000 times. This underscores the need to keep energy consumption in check for sustainable AI growth.
Highlighting the importance of emissions tracking, Vice President Al Gore remarked:
"The world has reached a tipping point on the climate crisis. In order to achieve a zero-carbon future, we need a comprehensive accounting of where pollution is coming from."
CarbonTracker AI is already making waves in manufacturing. For example, Carbon Re's Delta Zero platform, powered by CarbonTracker AI, has helped cement producers cut emissions by up to 10%. Adoption is growing fast, with 500 citations in academic and industry publications, 418 stars on GitHub, and 117,000 downloads on PyPI as of January 2025.
The tool is easy to integrate, thanks to its command-line interface and Python bindings, ensuring minimal disruption to existing sustainability efforts.
sbb-itb-f88cb20
5. Climate TRACE

Climate TRACE is a system designed to monitor global greenhouse gas emissions using satellite data and AI. By combining information from 300 satellites, over 11,100 sensors, and various public and commercial datasets, it offers detailed insights into emissions sources.
The platform tracks emissions across major sectors:
| Sector | Coverage | Global Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Power Generation | 25% of emissions | Tracks individual power plants |
| Manufacturing | 18% of emissions | Monitors factories and facilities |
| Fossil Fuel Operations | 16% of emissions | Identifies methane leaks |
| Transportation | 14% of emissions | Monitors road and air traffic |
| Agriculture | 14% of emissions | Tracks land use changes |
Climate TRACE now provides monthly emissions data for 1,813,558 sources across 72,000 regions, covering more than 90% of the world's cities. This approach makes it possible to monitor emissions at a granular level, from power plants to oil refineries.
The platform has revealed key trends in emissions. Between 2021 and 2022, global emissions grew by 1.5%, marking an 8.6% increase since 2015. Additionally, oil and gas emissions from production and transport were found to be three times higher than official reports suggest.
"Climate TRACE is the best game in town with data to tell us exactly where pollution is happening and the biggest opportunities to address inequalities and injustice."
The system has already influenced regional policies. For instance, in Western Cape, South Africa, it identified 42 beef and dairy feedlots near Cape Town, housing about 80,000 cattle. This data has helped shape local emission reduction strategies. In Jalisco, Mexico, its analysis of emissions from synthetic fertilizers provided new insights into how economic changes affect regional emissions.
"Leaders from the public and private sectors can now do what's never been possible before. They can look clearly at the causes of the climate crisis all the way down to the individual source. They can pinpoint where to take action almost immediately. With this inventory at our fingertips, there's no longer a valid excuse for anyone - businesses, governments, or otherwise - to turn a blind eye to the work that must be done to slash emissions significantly and quickly."
As of December 2023, Climate TRACE tracks over 352 million assets worldwide, a 4,400x increase in coverage, with free public access to its data. Next, learn how Aurora Solar AI applies similar technology to renewable energy solutions.
6. Aurora Solar AI
Aurora Solar AI is changing the game for solar installations, making the process faster and more efficient.
This platform uses AI to determine the best placement for solar panels, ensuring maximum energy output. In just 15 seconds, it can create highly accurate 3D roof models, which significantly speeds up project planning.
By combining advanced machine learning with HD Nearmap imagery and LIDAR shading technology, Aurora Solar AI produces detailed 3D models of homes and roofs. Some of its standout features include:
| Feature | Benefit | Time Saved |
|---|---|---|
| 3D Roof Modeling | Reduces change orders by 99% | 15 seconds per model |
| Design Generation | Produces proposal-ready designs | 32 seconds on average |
| Accuracy Rate | Matches or exceeds human designs (76–83%) | No site visit needed |
| Production Estimates | Delivers precise shading analysis | Instant results |
With over 1.6 million simulations completed, Aurora Solar AI matches or outperforms human designs 83% of the time for standard roofs and 76% for more complex ones. For instance, CertainTeed trained roofing specialists to become solar experts in just one day, and one dealer even closed a sale within the first week.
The platform also connects with IoT systems to optimize energy production and consumption remotely, eliminating the need for on-site visits and reducing environmental impact.
"In the history of the industry, we have never seen such strong price signaling, you know, in terms of market formation. So when I look at our own solutions and how AI has led those new products that we are launching… it's using this data."
– Chris Thompson, Vice President of Product and Technical Marketing, SolarEdge Technologies
Aurora Solar AI simplifies solar installations by cutting out site visits and refining design processes, making renewable energy more accessible and helping reduce the impact on the environment.
7. WindAI for Wind Farms
WindAI helps wind farms operate more efficiently by improving turbine performance by up to 20% and increasing their lifespan by 10%. It fine-tunes turbine settings, such as blade pitch and yaw angles, in real time to generate more energy while reducing wear and tear. This system enhances overall reliability in operations.
Key Features of WindAI
| Feature | Impact | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Predictive Maintenance | Lowers downtime | Saves $42,000–$48,000 per MW annually |
| Real-time Monitoring | 95% accuracy for ice issues | Protects turbines from damage |
| Weather Pattern Analysis | Cuts costs by 15% | Improves energy output |
| Visual Inspection | 80% accuracy for lightning | Ensures quick repairs |
In China, AI-powered visual inspection systems are widely used, achieving over 95% precision in spotting ice buildup and cracks, as well as 80% accuracy for detecting lightning strikes.
By combining IoT sensors with advanced analytics, WindAI identifies problems early, minimizing repair expenses and downtime. For example, GE's adoption of AI tools for installation logistics has cut wind turbine installation costs by 10%. Vibration analysis also plays a crucial role, identifying early wear in critical parts like gearboxes and bearings.
WindAI works seamlessly with existing wind farm management software, enabling automated decisions about power output and distribution. Its big data capabilities further optimize farm performance. Additionally, it simplifies energy storage and distribution, making it a key resource for modern wind farm operations. Up next, learn how Rainforest Connection AI uses similar technology to protect ecosystems.
8. Rainforest Connection AI
Rainforest Connection (RFCx) uses AI-powered acoustic technology to protect forests in the fight against climate change. Their system, called Guardian, offers real-time monitoring, showcasing how AI can play a crucial role in safeguarding ecosystems.
Guardian is installed in 587 forest canopies across 37 countries, covering 736,200 hectares. Each device listens to the forest, recording sounds within a range of 50–1,500 meters. It can detect everything from chainsaws to subtle changes in animal calls.
| Monitoring Capabilities | Impact Statistics |
|---|---|
| Protected Land | 736,200 hectares |
| Audio Files Recorded | 160 million |
| Species Identified | 4,208 total |
| Endangered Species Tracked | 408 threatened species |
| AI Detection Capability | 955 species automatically |
This system helps combat illegal logging, an industry valued at US$50–US$150 billion annually. Topher White, CEO and Founder of RFCx, explains:
"Arm technology allows us to pick up all the sound of the forest 24 hours a day, package it up and send it up into the cloud over any network that's available, where we then use AI to analyse it. It plays a vital role in this constant connection between us and the rainforest and allows us to alert rangers of environmental threats in real time."
RFCx has partnered with Hitachi to enhance its AI algorithm, which predicts illegal logging with 96% accuracy up to five days in advance by analyzing changes in animal behavior. This technology has the potential to reduce illegal logging by 35%.
The system has proven effective across various regions. For instance, it monitors endangered parrots in Ecuador and identifies high-risk poaching times in Africa, helping rangers act more efficiently. Considering deforestation is responsible for 17% of global carbon emissions, such efforts are essential for addressing climate change.
"There is no solution to climate change unless we protect rainforests. That doesn't mean that we regrow what we've lost. That doesn't mean we can cut them down and then grow them back. It means they have to stay in place, as they are. That's a fact, and it's this fact that drives us."
9. Wildlife Insights
Wildlife Insights leverages Google's open-source TensorFlow to analyze millions of camera trap images, offering a powerful tool for tracking and protecting wildlife in the face of climate challenges.
The platform's AI has been trained on over 35 million images covering 1,295 species. Its advanced algorithms deliver highly accurate animal identification:
| AI Performance Metrics | Accuracy Rate |
|---|---|
| Blank Image Detection | 94% with less than 2% error rate |
| Animal Presence Detection | 97% probability |
| Species Identification | 80–99% for well-documented species |
| Total Species Coverage | 1,295 species + 237 taxonomic classes |
Wildlife Insights has drastically improved efficiency for conservation projects. For example, the University of Queensland processed more than 130,000 camera trap images in just one hour, with a team of around 50 students reviewing the AI's classifications.
WWF Colombia uses the platform to maintain a jaguar conservation corridor in Guaviare, connecting habitats across countries from Mexico to Argentina. Similarly, Colombia's Camera Trapping Network and the Humboldt Institute rely on it for large-scale studies of mammals and birds.
"Big data and AI have transformed endangered species conservation. Wildlife Insights brings millions of hidden images into focus to drive critical conservation decisions", says Margaret Kinnaird, WWF Wildlife Practice Leader.
Wildlife Insights serves conservationists, businesses, and policymakers by seamlessly integrating into climate-related efforts. Conservation groups can track wildlife recovery in reforested areas, companies can verify their ecological impact, and governments can craft data-driven conservation policies.
Its efficient image processing also supports climate research. Scientists can use it to predict climate trends, while land managers can detect early signs of ecosystem changes through shifts in wildlife populations. These capabilities make Wildlife Insights a key tool in addressing climate challenges.
Conclusion
Combining AI tools with efforts to address climate change is reshaping how we tackle environmental challenges across various industries. These nine tools are changing the game by improving energy use and cutting emissions. But this progress doesn’t come without trade-offs.
One major concern is the environmental toll of AI itself. For instance, training large models like GPT-3 required over 1,200 MWh of energy - enough to power one million American homes for an hour. Roberto Verdecchia, an Assistant Professor at the University of Florence, highlights this issue:
"In the race to produce faster and more-accurate AI models, environmental sustainability is often regarded as a second-class citizen."
To balance the advantages of AI with its environmental costs, organizations should prioritize three areas:
| Focus Area | Current Impact | Future Potential |
|---|---|---|
| Emissions Monitoring | AI tracks CO₂ and methane emissions with precision | Real-time data and improved attribution for better decision-making |
| Resource Optimization | Boosts energy efficiency across industries | Integration with renewable energy systems and smarter grid management |
| Ecosystem Protection | Tracks wildlife and habitat changes, offering early alerts | Broader coverage and more accurate predictions for safeguarding ecosystems |
The impact of these tools goes beyond technology. IBM's Green Horizon Project, for example, has used AI to analyze weather patterns, industrial emissions, and traffic in Beijing, resulting in cleaner air.
However, as Sam Altman, CEO of OpenAI, warns:
"Future AI research and development will consume much more power than we expect."


